- Home
- Trauma-Informed Education
- Trauma Overview
-
#onecaringadult
- #Onecaringadult Allegany County App
- #onecaringadult- Academic Stress
- #onecaringadult- Alcohol and Other Drugs
- #onecaringadult- Bullying
- #onecaringadult- LGBTQ+
- #onecaringadult- Childhood Neglect
- #onecaringadult- E-Cigarettes and Vaping
- #onecaringadult- Eating Disorders
- #onecaringadult- Mental Health
- #onecaringadult- Online Sexual Exploitation
- #onecaringadult- Non-Suicidal Self-Injury
- #onecaringadult- Sexual Abuse
- #onecaringadult- Sexually Transmitted Infections
- #onecaringadult- Suicide Prevention
- #onecaringadult- Teen Dating Violence
- #onecaringadult- Teen Pregnancy
- #onecaringadult- Toxic Stress
- #onecaringadult- Vaping & E-Cigarettes
- #onecaringfriend
- Trauma-Informed Resources
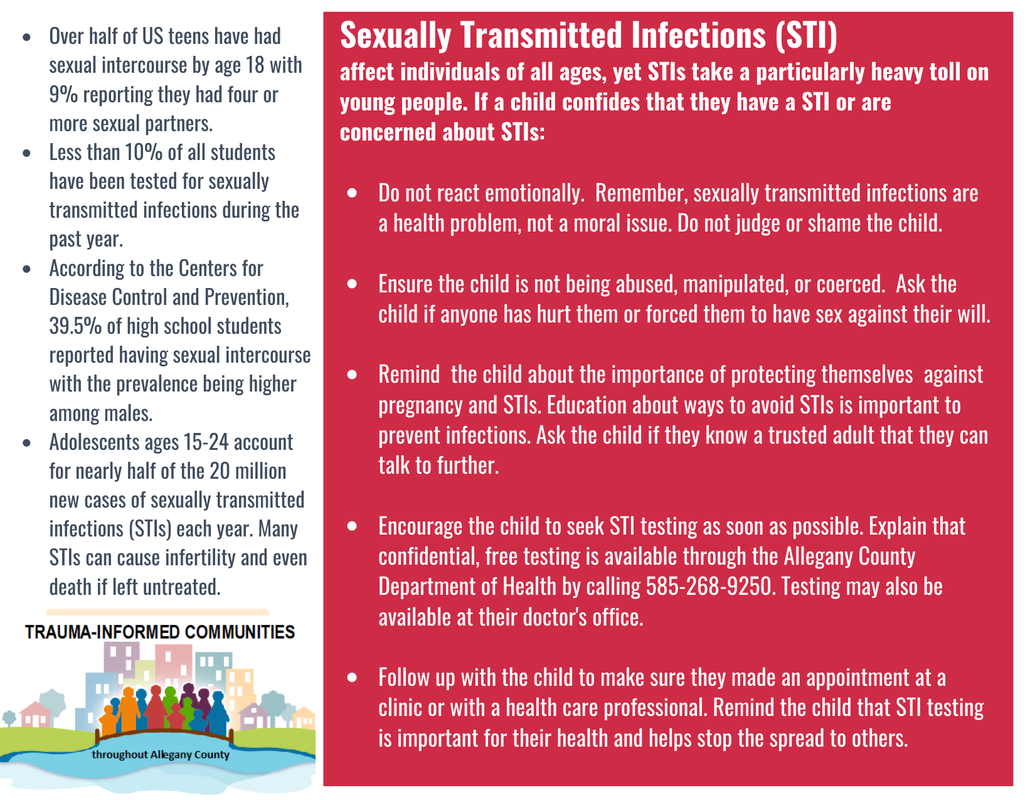
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS
STIs are diseases that are passed from one person to another through sexual contact. These include chlamydia, gonorrhea, genital herpes, human papillomavirus (HPV), syphilis, and HIV. Many of these STIs do not show symptoms for a long time. Even without symptoms, they can still be harmful and passed on during sex. STIs are common, especially among young people. There were 26 million new sexually transmitted infections in 2018 in the United States. About half of these infections are in people between the ages of 15 and 24.
|
Young people are at greater risk of getting an STI for several reasons:
|
|
Source: Center for Disease Control
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
|
Recognizing Signs of STIs
Many STIs have no signs or symptoms (asymptomatic). Even with no symptoms, however, you can pass the infection to your sex partners. Learn about the signs and symptoms of the most common STIs below:
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a bacterial infection of your genital tract. Chlamydia may be difficult to detect because early-stage infections often cause few or no signs and symptoms. When they do occur, symptoms usually start one to three weeks after you've been exposed to chlamydia and may be mild and pass quickly. Signs and symptoms may include:
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a bacterial infection of your genital tract. The bacteria can also grow in your mouth, throat, eyes and anus. The first gonorrhea symptoms generally appear within 10 days after exposure. However, some people may be infected for months before signs or symptoms occur. Signs and symptoms of gonorrhea may include:
Tricomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is a common STI caused by a microscopic, one-celled parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. This organism spreads during sexual intercourse with someone who already has the infection. The organism usually infects the urinary tract in men, but often causes no symptoms. Trichomoniasis typically infects the vagina in women. When trichomoniasis causes symptoms, they may appear within five to 28 days of exposure and range from mild irritation to severe inflammation. Signs and symptoms may include:
Genital herpes
Genital herpes is a highly contagious STI caused by a type of the herpes simplex virus (HSV) that enters your body through small breaks in your skin or mucous membranes. Most people with HSV never know they have it, because they have no signs or symptoms or the signs and symptoms are so mild they go unnoticed. When signs and symptoms are noticeable, the first episode is generally the worst. Some people never have a second episode. Others, however, can have recurrent episodes for decades. When present, genital herpes signs and symptoms may include:
In some cases, the infection can be active and contagious even when sores aren't present. Human papillomavirus (HPV)
HPV infection is one of the most common types of STIs. Some forms of HPV put women at high risk of cervical cancer. Other forms cause genital warts. HPV usually has no signs or symptoms. The signs and symptoms of genital warts include:
hepatitis
Hepatitis A, hepatitis B and hepatitis C are all contagious viral infections that affect your liver. Hepatitis B and C are the most serious of the three, but each can cause your liver to become inflamed. Some people never develop signs or symptoms. But for those who do, signs and symptoms may occur several weeks after exposure and may include:
Syphilis
Syphilis is a bacterial infection. The disease affects your genitals, skin and mucous membranes, but it can also involve many other parts of your body, including your brain and your heart. The signs and symptoms of syphilis may occur in three stages — primary, secondary, and tertiary. Some people also experience latent syphilis, in which blood tests are positive for the bacteria but no symptoms are present. At first, only a small, painless sore (chancre) may be present at the site of infection, usually the genitals, rectum, tongue or lips. As the disease worsens, symptoms may include:
Some of the signs and symptoms of late-stage syphilis include:
|
Learn More About Youth and STIs
|
|
Source: Mayo Clinic
Preventing STIs
Abstinence from all forms of sex including vaginal and anal intercourse as well as oral sex is the only 100 percent effective way to prevent an STI. However, for sexually active teens, there are other ways to practice having safe sex for STI prevention.
Source: TeenHelp.com
|
Helpful Links
Talking with Your Teens about Sex: Going Beyond "the Talk" (cdc.gov)
University of Rochester Medical Center SafeTeens: Your Guide To Sex Ed and Healthy Relationships. Talking to Your Kids About STDs (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth What Are STDs? | Sexually Transmitted Diseases Information (plannedparenthood.org) Resources for parents (shiftnc.org) Parents (ashasexualhealth.org) New York State Department of Health Allegany County Department of Health |
- Home
- Trauma-Informed Education
- Trauma Overview
-
#onecaringadult
- #Onecaringadult Allegany County App
- #onecaringadult- Academic Stress
- #onecaringadult- Alcohol and Other Drugs
- #onecaringadult- Bullying
- #onecaringadult- LGBTQ+
- #onecaringadult- Childhood Neglect
- #onecaringadult- E-Cigarettes and Vaping
- #onecaringadult- Eating Disorders
- #onecaringadult- Mental Health
- #onecaringadult- Online Sexual Exploitation
- #onecaringadult- Non-Suicidal Self-Injury
- #onecaringadult- Sexual Abuse
- #onecaringadult- Sexually Transmitted Infections
- #onecaringadult- Suicide Prevention
- #onecaringadult- Teen Dating Violence
- #onecaringadult- Teen Pregnancy
- #onecaringadult- Toxic Stress
- #onecaringadult- Vaping & E-Cigarettes
- #onecaringfriend
- Trauma-Informed Resources